Author: Thushara
Port Security
Switch port security monitors a port to restrict the number of MAC addresses associated with that port in the Layer 2 switching table. It can also enforce a restriction for only certain MAC addresses to be reachable out the port.
Instead of automatically adding a Layer 2 switching table entry for the source MAC and port number, now the switch considers the port security configuration and checks whether it allows that entry or not.
We implement the port-security to avoid MAC flooding & MAC-address spoofing attacks.
MAC flooding
Attacker connected to the switch port will generate & send thousands of frames with different source MAC addresses.
Total MAC-address space available in a switch is 6003, if the whole MAC-address table is filled then the switch will times out older entries.
If the switch receives frames destined for those MACs that are no longer in the table, the switch will do the unicast flooding(floods the frames out all ports).
This attack can be launched for the malicious purpose of collecting a broad sample of traffic or as a denial of service (DoS) attack.
so with the port-security we can limit the maximum number of MAC-address that can be learned on a port.

MAC-address spoofing
An attacker could also claim to be the same MAC address as a legitimate user by simply sending a frame with that same MAC address. As a result, the switch would update its switching table and send frames to the attacker.
So With port-security you can bind MAC-address on a port, so that you can allow only those MAC addresses on the switchport to access the network. Even though it is not secure, because we can change the MAC-address of the PC.
Maximum number of MAC-address that can be binded with the port are 1 by default. But we can increase this value to allow more users to access.
If a violations occurred then by default port-security puts the port into Error-disable state.

- There are two types of aging for MAC-addresses:
- Absolute aging:
- Means it delete the MAC addresses from the Port-address table after a certain period of time, even it don’t care that the MAC-address is active or not.
- Inactivity aging:
- If the MAC-address is not active for certain period of time, then it will remove from the Port-address table.
- Absolute aging:
We can enable port-security only on access ports or trunk ports not on Dynamic ports.
So first of all we have to forcefully made the port as access/trunk.
- How MAC-address can be binded in port-security on a port?
- Dynamic binding – Configuration saves in running-configuration.
- static binding – Configuration saves in startup-Configuration. (Means these MAC-address remains after the reboot also)
- Dynamic with sticky – After learning MAC-address dynamically, switch binds the MAC & saves it in startup-Configuration.
- When you configure Dynamic with sticky then it shows as Secure-sticky.
- In trunk ports we can bind MAC-address to the different VLANs.
- To recover from Error-disable state there are two ways:
- Manually: (shutdown & no shutdown)
- Automatically: (Using error disable recovery) It is disable by default.
- Violation modes in port-security:
- Shutdown – Enables by default
- Protect – Doesn’t generate log messages & violation count is not kept.
- Restrict – Generates the log messages(SNMP traps) & violation count is kept.
- Both the protect & restrict modes do not put the port into error-disable state when a violation occurs.
- Even when violation are being done,still the port remains up. But the violation frames will be dropped.

- only the first two commands are required for port security. With just those two commands, a port allows the first-learned MAC address to be used, but no others. If that MAC address times out of the CAM, another MAC address can be learned on that port, but only one is allowed at a time.
- The next two commands in the table allow for the definition of MAC addresses.
- The third command statically defines the permitted MAC addresses.
- The fourth command allows for sticky learning. Sticky learning tells the switch to learn the MACs dynamically
- The last command in the table tells the switch what to do when violations occur.
Note: The “switchport port-security maximum x” command would be required to
allow more than one MAC address, with x being the maximum number
VPN – Virtual Private Network
- What is a VPN?
- It is a logical connection between two entities typically secure over an unsecure channel.
- Virtual – Private network traffic transported over ‘public’ network
- A sort of tunneling is created to achieve that.
- Private – Traffic is isolated and optionally encrypted.
- Why do we need VPNs?
- Cost savings
- Compatible with any transport technology (traffic issues)
- Security
- In earlier 1980s they mainly focused on providing services not on security.
- After some attacks, they came to know that security is the essential thing for shared medium.
- Eavesdropping attack:
- Eavesdropping is the unauthorized real-time interception of a private communication, such as a phone call, instant message, and videoconference or fax transmission.
- The term eavesdrop derives from the practice of actually standing under the eaves of a house, listening to conversations inside.
- The attacker is going to access the content of the packet (Man in the middle attack) using Wireshark, SPAN, RSPAN…etc.
- Masquerading attack:
- A masquerade attack is an attack that uses a fake identity, such as a network identity to gain unauthorized access to personal computer information through legitimate access identification.
- If an authorization process is not fully protected, it can become extremely vulnerable to a masquerade attack.
- In this attack, the attacker is going to hide his own identity and pretend to become someone else
- Phishing attack:
- Phishing is a type of social engineering attack often used to steal user data, including login credentials and credit card numbers.
- It occurs when an attacker, masquerading as a trusted entity, dupes a victim into opening an email, instant message, or text message.
- The recipient is then tricked into clicking a malicious link, which can lead to the revealing of sensitive information.
- Now it is not allowed.
- VPN Examples:
- VLAN
- Frame-relay PVC (via DLCI)
- MPLS VPN (layer2/layer3)
- AToM
- GRE
- IPsec
- SSL
- MACsec
- What are the types of VPN?
- Site to Site VPN (supported by Router & ASA)
- Between two VPN gateways (router-router/firewall-firewall)
- Statically or dynamically assigned IPv4/IPv6 addresses
- IPsec is the framework used to secure data
- IKEv1 or IKEv2 are used to dynamically negotiate the tunnel
- Some vendors, not Cisco also offer SSL VPN
- Remote VPN (Router & ASA)
- Between a VPN gateway and an end-user/device
- VPN gateway has a static IPv4/IPv6 address
- End-user has a dynamic IPv4/IPv6 address in general
- Client-based
- IPsec (IKEv1 or IKEv2) and SSL VPN (TSLv1 or SSLv3)
- Clientless, browser-based
- SSL VPN only (TLSv1 or SSLv3)
- DMVPN (Router)
- GETVPN (Router)
- FIEX VPN (Router & ASA)
- SSL VPN (Router & ASA)
- Site to Site VPN (supported by Router & ASA)
- Features of VPN:
- Confidentiality
- Integrity
- Authentication
- Anti-replay
- Confidentiality:
- It can be achieved only by CIPHER.
- CIPHER: It is used to convert the plain text traffic into unreadable format.
- CIPHER types:
- Stream CIPHER: Bit by Bit encryption
- This is very CPU intensive work, so it is not supported by Cisco
- This method can be used for highly secure communication. (Military, Navy)
- Suppose we has to send 10 bits data then it runs the algorithm 10 times for encryption & 10 times for decryption, total 20 times.
- Stream CIPHER: Bit by Bit encryption
Important Well known Ports
| PORT Number | PROTOCOL | Description |
| 1 | TCP | |
| 7 | ICMP Echo | |
| 20 | FTP Data | |
| 21 | FTP Control | |
| 22 | SSH | |
| 23 | TELNET | |
| 25 | SMTP | Simple Mail Tranfer Protocol |
| 49 | TACACS+ | |
| 67 | DHCP Server | |
| 68 | DHCP Client | |
| 69 | TFTP | Trivial File Transfer Protocol |
| 110 | POP3 | Post Office Protocol |
| 115 | SFTP | Simple File Transfer Protocol |
| 123 | NTP | Network Time Protocol |
| 143 | IMAP | Internet Message Access Protocol |
| 161 | SNMP | Simple Network Management Protocol |
| 162 | SNMP TRAP | |
| 179 | BGP | Border Gateway Protocol |
| 220 | IMAP version 3 | |
| 389 | LDAP | Lightweight Directory Access Protocol |
| 443 | HTTPS | Hypertext Transfer Protocol over TLS/SSL |
| 500 | ISAKMP | Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP) / Internet Key Exchange (IKE) |
| 514 | Syslog | |
| 520 | RIP | Routing Information Protocol |
| 521 | RIPng | For IPV6 |
| 530 | RPC | Remote Procedure Call |
| 546 | DHCPv6 client | |
| 547 | DHCPv6 Server | |
| 554 | RTSP | Real Time Streaming Protocol |
| 585 | IMAP over TLS/SSL | Legacy (New Port 993) |
| 587 | SMTP over TLS | |
| 601 | Syslog | Reliable Syslog Service |
| 636 | LDAPS | Lightweight Directory Access Protocol over TLS/SSL |
| 646 | LDP | Label Distribution Protocol |
| 989 | FTPS (data) | |
| 990 | FTPS (control) | |
| 992 | TELNET over TLS/SSL | |
| 993 | IMAP over TLS/SSL | |
| 995 | POP3 over TLS/SSL |
Implementing F5 Local Traffic Manager (LTM)
Initializing F5 BIG IP Virtual Edison (VE)
- Obtaining the OVA installer
- Deploying the BIG IP OVA installer
- Licensing BIG IP
- Initial Setup
Obtaining the OVA installer
BIG IP Virtual Edition (VE) comes in 3 variations
- Free Trial
- Lab License
- Full Featured Evaluation
The main difference between these are what are the particular modules what we are able to activate once we install BIGIP & what is going to be the throughput level of individual modules. Lab license which allows to use the modules that is LTM (Local Traffic Manager), GTM (Global Traffic Manager), & additional modules ASM (Application security modules).
Note: For more information see…
- F5.com > Free Trial
Deploying the Big IP OVA installer
- Requires a Supported Hypervisor (VMware ESXI/VSphere/KVM)
- More info at BIGIP Virtual Edition Setup Guide for VMware ESXI
CLI – to set the basic management address to access the GUI
By default the installer is going to assume that we have 4 different network segments.
- Management
- Internal servers (Web/FTP servers) – data plane
- External – data plane
- HA(High availability)Failover

Default login credentials
- CLI – root/default
- GUI – admin/admin
Setup:
- Take the cli console & login with the default credentials.
- Type configure to configure management IP address to get access to GUI.
- By default DHCP service is enabled on management interface, we can disable DHCP & configure the static IP address.
- If the management interface is on different subnet other than the admin user machine, we need to configure the default-gateway or else no need.
Licensing BIG IP

- All the BIGIP setup requires the license.
- License can be installed automatically or manually
- Automatic assumes BIGIP has Internet connectivity
- Manual allows copy and paste of license key

- Login to the GUI & setup the license either for free trail or full functionality.
- We can generate a trail license key from the F5.com post login.
- So that you will receive the license key on the email, copy the code and paste on the license tab and click next.
- If LTM not having the internet connection do it manually else select automatic.
- For manual setup the LTM will generate a code (Dossier – certificate), copy that certificate & paste it in the licensing website & click next.


- Website will returns the license file to install, either we can copy & paste the entire license text on the LTM or else we can download & upload to LTM.



- We should see it’s now going to determine which particular modules are going to be licensed on this box.
- We can see the activated (licensed) modules in the Resource provisioning under setup utility tab.

- Under Resource provisioning we can control the reservations of CPU/Memory resource for the individual modules.
- If the box is licensed for only LTM then on the drop down box of resource provisioning we can select dedicated so that it will allocate dedicated resources to LTM module.

Initial Setup
GUI Setup Utility walks through basic options


- Under setup utility –> Platform (do initial configuration)
- Edit the management port configuration & Hostname(should be FQDN).
- User Administration (Root & Admin accounts)- default roles
- We can disable to root login if we don’t want anyone to use cli.
- Admin user is authorized for only GUI by default not for the CLI.
- SSH access (enabled by default)

- Standard network configuration:
- Redundancy – High availability
- Options to select how we going to do the network high availability.
- Both config-sync & HA failover
- By default failover method is based on the network. Else we can choose serial cable method if we are using a physical BIGIP box that has a dedicated failover port on the front of the box like one of the older DB9 port we will plug back to back each other between the two traffic managers if the primary one fails the secondary one will promote itself to the active state.
- Redundancy – High availability

VLAN – Internal network configuration & Internal VLAN configuration.
- Internal network configuration:
- Self IP config (the local internal IP address)
- Floating IP config (the shared VIP internal)
- Port lockdown – what are the services that BIGIP are going to listen on the inside interface. By default it does listen for management traffic(from the internal network you can access the GUI of the LTM by default)

- Internal VLAN configuration:
- The physical Ethernet interfaces(default 4 network segments) will define as 1.0,1.1,1.2 & 1.3.
- Interface 1.0 won’t show here as it already configured to management access.
- login to cli as a root user & check the interface
- command – ifconfig | less
- If you not sure how these virtual Ethernet interfaces mapped on the hypervisor level we can look at the mac-address that auto generated on the hypervisor.
- From the real physical box deployment this is going to determine how you physically wired the BIGIP into the Ethernet switches.
- do you want to run dedicated links to internal & external (one physical switch in the inside & one physical switch in the outside) or you are running both internal & external switches as one logical box & then separate the traffic based on the VLAN tags.
- If you are connecting the internal port to the access switch port then select Untagged.
- If you are connecting the internal port to the trunk switch port then select tagged.
- From the logical networking point of view this is the first big detail we need to make sure that is correctly mapped out. The virtual interfaces to the physical interfaces mapping otherwise BIGIP won’t accept the traffic in correct direction.
- Select the VLAN interface 1.1
- VLAN tagging – untagged.

- External network configuration:
- Create the external VLAN(check the external VLAN in given option)
- Self IP config & port lock down (none because we won’t give management access to outside users).
- Default gateway
- Floating IP (the shared VIP between the Active & the standby peer) same IP on both the peers
- External VLAN configuration:
- Select the VLAN interface 1.2
- VLAN tagging – untagged.

- High availability network configuration:
- HA VLAN not going to be routable to the rest of the network (locally significant b/w the failover peer) you can think this like an feasible serial cable plugged in the two peers that they going to be synchronizing the connection states form the active to the standby box & also going to be one of the interfaces that tracking durability.
- If the primary box goes down the secondary will promote itself & start actively forward traffic.
- Create HA VLAN
- Self IP config.
- High availability VLAN configuration:
- Select the VLAN interface 1.3
- VLAN tagging – untagged.

- NTP server configuration for synchronization of time for the logs.
- The time is going to be significant because there is a valid time for the certificate to be used or whether it’s going to be revoked.
- Same for the DNS server configuration.

- Config sync configuration:
- This is going to be how the primary box sense its changes down to the secondary.
- Select the HA VLAN (configured before).
- Technically we can use any of the configured VLAN as long as the peer aggress on what the source & destination is going to be, because the primary box should be listening to the secondary & wise versa.
- This is going to be how the primary box sense its changes down to the secondary.

- Failover – by default we are checking for the both the management IP connectivity & the HA.

- Mirroring configuration: – Default HA IP connectivity.

- Active standby pair:
- this is where we actually join the HA pair (The primary & secondary)
- Primary box is where we make all our configuration changes & then those going to synchronize down to the secondary.
- From the traffic point of view we can define below modes:
- Active standby
- Active Active

- Discover peer:
- Enter the remote device credentials:
- Device IP address – HA interface IP address.
- Remote Admin login credentials.
- We can see they will install the certificate between them so we are creating a trust relationship between them. This is going to prevent any other type of BIGIP box trying to synchronize the config without having this particular RSA key.
- The certificate is self-signed by default(signed from local host & local domain)
- After finishing go to the secondary box & click finished.
- Now we can see one box will be elected as primary & the other as secondary.
- From the configuration & traffic point of view if we are doing active standby it doesn’t matter which one is active & which one is standby. Because from the client point of view they don’t know there is multiple devices in the middle they both load balancing the traffic. Since we have the shared floating VIP address between them as long as the inside servers using that VIP as their gateway then the traffic should be able to load balanced in & correctly returned out through the local traffic manager as the replies are go back to the clients.



- Awaiting the initial sync: talking about the config that was setting up between the HA peers.
- If you see the primary box for the failover-group the failover is going to be manual synchronization
- If u make a config change (create a Virtual server or a pool) on the primary box those are not automatically replicated down to the standby (secondary).
- We can change this to automatic synchronization, but in the real deployment it’s not recommended.

- To force the sync:
- Device management -> Overview & click the device you want to sync -> select sync option (sync to the group) & click Sync.
- Then we will the awaiting initial sync icon turns to green which means config synced.

Then reload the page to see the status synced.

CCNA Security Day 1
- What is Data?
- Data is a Piece of information.
- Example:
- cisco : Data
- 1234 : Data
- Example:
- Data is a Piece of information.
- Types of Data?
- There are two types of data:
- Data in Motion
- When the information is moving from one location to another location.
- Data at Rest
- When the information is not moving from one location to another location.
- Data in Motion
- There are two types of data:
- How to secure Data at Rest?
- Physical security – put the pen drive / hard disk in locker.
- Logical security – put a password to pen drive.
- Here we learn one thing from CCNA to CCIE Security.
- How to secure Data in Motion?
- To secure DIM (Data in motion)
- We follow a model called CIA model.
- C – Confidentiality
- I – Integrity
- A – Availability
- How to secure Data in Motion?
- Confidentiality: Only authorized users can read the information.
- Integrity: Only authorized users can change the data.
- ( When the information is moving from one location to another location it should not be tampered or change )
- For that there is CRC ( Cyclic Redundancy Check ) in IP packet
- Availability: The information should be available to only authorized users.
- ( When a user login with his credentials, he should not be provided by other users data )
- Protecting the Infrastructure:
- NFP – Network Foundation Protection
- ( Idea of categorizing specific network functions and then implementing the correct security measures to build the best security for our networks )
- Broken the Basic network Infrastructure into four basic elements.
- NFP – Network Foundation Protection
- How many types of Traffic?
- There are three types of traffic:
- Host Type: Traffic that is destined to the device.
- Ex: If we telnet to the device then the traffic is called host traffic (TELNET, SSH, HTTP, HTTPS…etc.)
- Transit Type: The traffic that is going through the device.
- Ex: Any traffic forwarded by FIB ( Forward information base ) table
- CEF exception traffic Type: Where TTL is 1 or Less than 1 or non IP packets.
- Ex: ARP, BPDU…etc.
- Host Type: Traffic that is destined to the device.
- There are three types of traffic:
- Note: Cisco says that.
- You cannot implement security in traffic types.
- But we can only implement the security in traffic plane ( means Functionality )
- Rather than categorizing the traffic types it’s better to categorize the traffic based on functionality.
- How many types of traffic planes:
- Ans. There are four types of traffic planes:
- Management Plane: The traffic that is generated by the user to the device for the management perspective.
- Ex: TELNET, SSH, HTTP, HTTPS, SNMP, SYSLOG, CCP, etc.
- Data Plane: The traffic that is generated by the user for the user.
- Ex: PING, FTP…etc.
- Control Plane: The traffic that is generated by the device for the device.
- Ex: Routing Protocols Data.
- Service Plane: The traffic that going through the device but it requires special attention from the CPU.
- Ex: NAT on the router / VPN.
- If you want to perform NAT then the router want to inspect the transit data.
- Management Plane: The traffic that is generated by the user to the device for the management perspective.
- Ans. There are four types of traffic planes:
GNS3 Client & Server installation on windows 10
Use below links to download GNS3 client, GNS3-VM & VMware.
We can download GNS3-VM in the GNS3-2.2.11-all-in-one-regular.exe itself but if you want to download separately please use the above link.
Click here to navigate to the GNS3 releases, there we can download all new & previous of GNS3 & GNS vm.
In case if you do not have VMWare installed on your machine, you can download VMWare Workstation, before starting this exercise this should be installed on your device.
VMware provides 30 days evaluation (free trail). Click on the below link to download the Key-Generator.
Note: Before downloading the Key-Generator you have to disable the windows defender (Firewall) & real time protection on windows 10.

Step:1
Install the VMware that downloaded before & insert the license activation key at the end of installation.
Step:2
Install the GNS3-2.2.11-all-in-one-regular.exe
While installing you will find the below options:

- GNS3 Desktop:
- It is a client application which provides the GUI interface to the user.
- It should connect to the GNS3 server to run Images (Routers/Switches/Firewalls…etc.)
- It itself having a local server which can run Ethernet bridge, VPC (virtual PC)…Etc. Local server also be used to connect the GNS3 to the physical machine Ethernet(NIC) both LAN & WIFI, so that we can access the internet from network devices which are running in GNS3.
- This setup will works good in Linux OS but Windows can’t natively run IOU or KVM.
- GNS3 VM:
- It is basically a GNS3 server which is already installed on a Linux OS.
- This GNS3 VM needs to be imported to either VMware Workstation/ESXI/Hyper-V/KVM or Virtualbox.
- Based on the virtualization platform where it’s getting installed the respective OS needs to be downloaded from the GNS3 official site.
- It lets Windows users run IOS/IOU/KVM images within it, since Windows can’t natively run IOU or KVM. Qemu VMs will sometimes work in Windows, but KVM is part of the Linux kernel, so they can’t use it, without that GNS3-VM.
- Remote-Server:
- gns3-gui.exe runs on your local machine, gns3-server.exe runs on a remote machine.
- Which means if the local machine is not having the required hardware configuration then we can point the GNS3 client to use the GNS3 VM which is installed on remote server.
- We can configure multiple remote servers in GNS3 client & all of them works together.
- GNS3 Web UI:
- Same as GNS3 desktop it provides the GUI interface to the user but through the Web browser, no need to install the GNS3 Desktop.
- It’s just launched few months back, still running on beta version (not stable).
- We need to install protocol handlers to get the console access of the devices.
- With the help of protocol handlers the Web browser can communicate with the respective console applications (putty/VNC).
- Web-console is the other option to take the console access of the devices, the console of the device can open in the same web page or in new tab.
- GNS3 Web Client:
- This package will install the protocol handlers for the GNS3 Web UI as discussed above.
- Without installing this package we can’t use native console application from GNS3 Web UI
Import GNS3 VM into VMware Workstation:
- In this section, you will learn how to import the GNS3 VM into VMware Workstation on your local Windows PC.
- Extract the downloaded .zip archive:
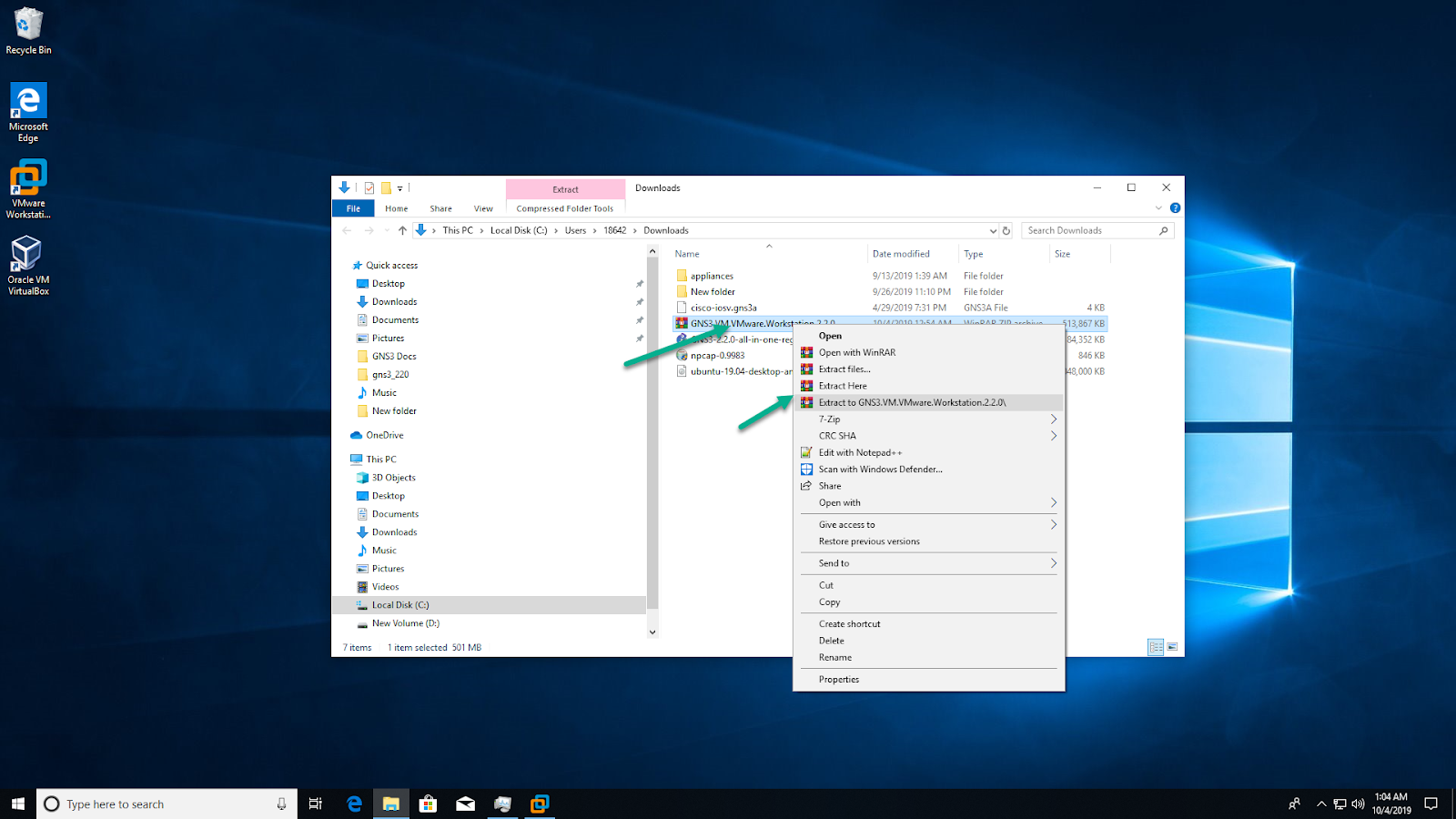
This extracts the “GNS3 VM.ova” file stored within the compressed archive, in order to import it into VMware Workstation.
In VMware Workstation, click ‘Open a Virtual Machine’:
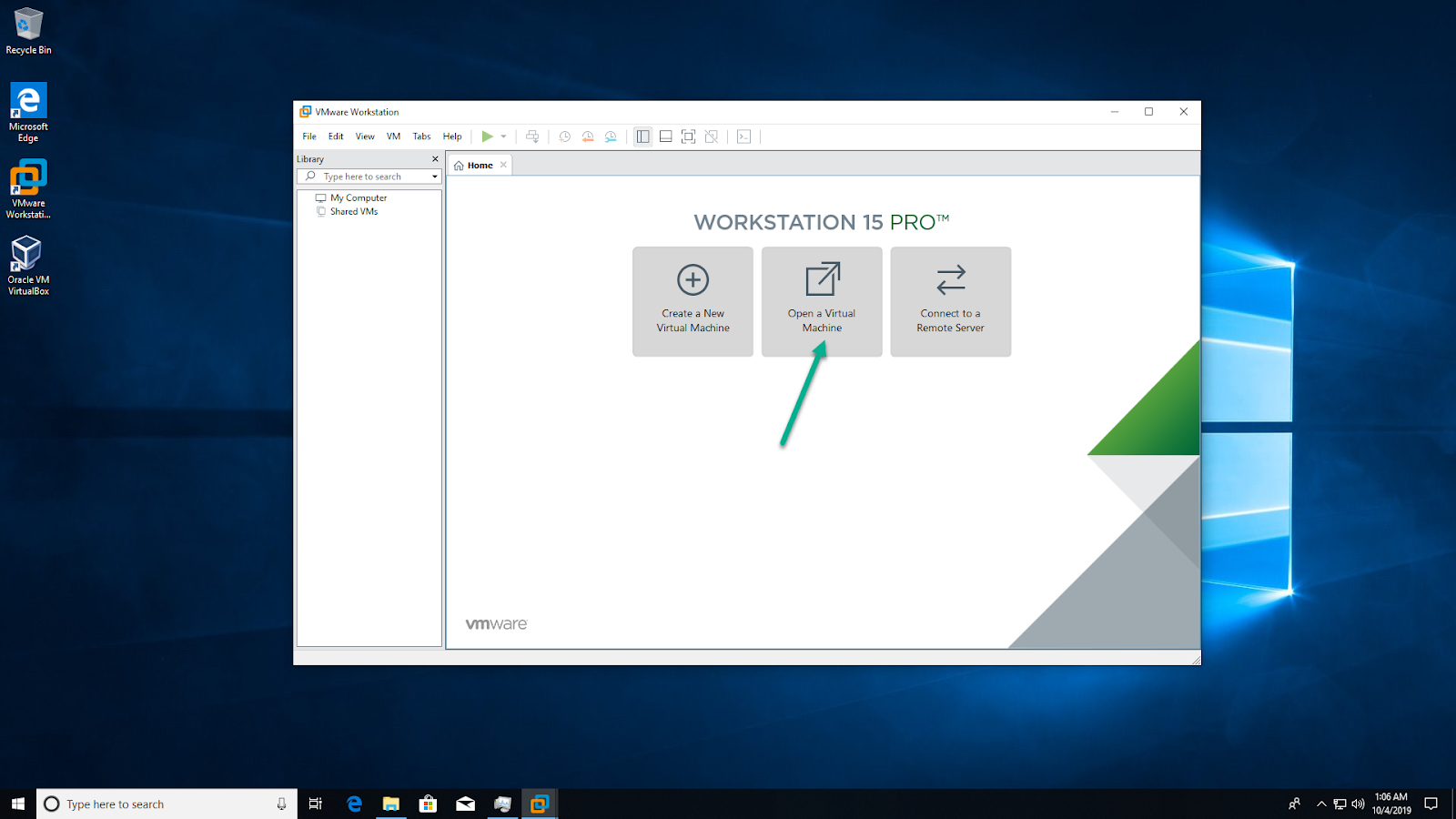
Navigate to the directory where the extracted GNS3 VM.ova is located, and click ‘Open’ to open the OVA Or else we can directly open the GNS3 VM.ova file(by double click) it will redirect to the VMware.
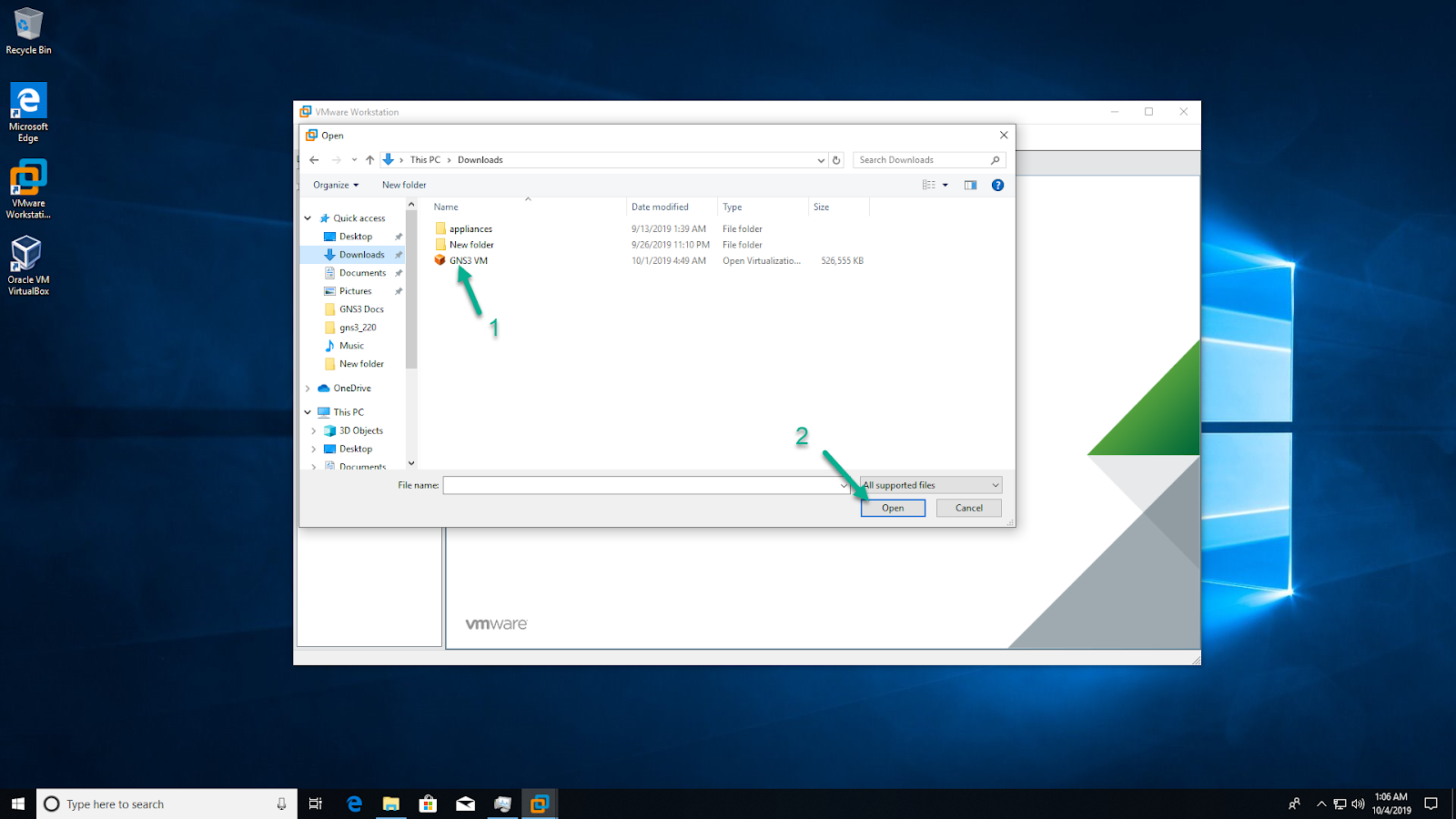
Leave the virtual machine name as ‘GNS3 VM’, and click ‘Import’:
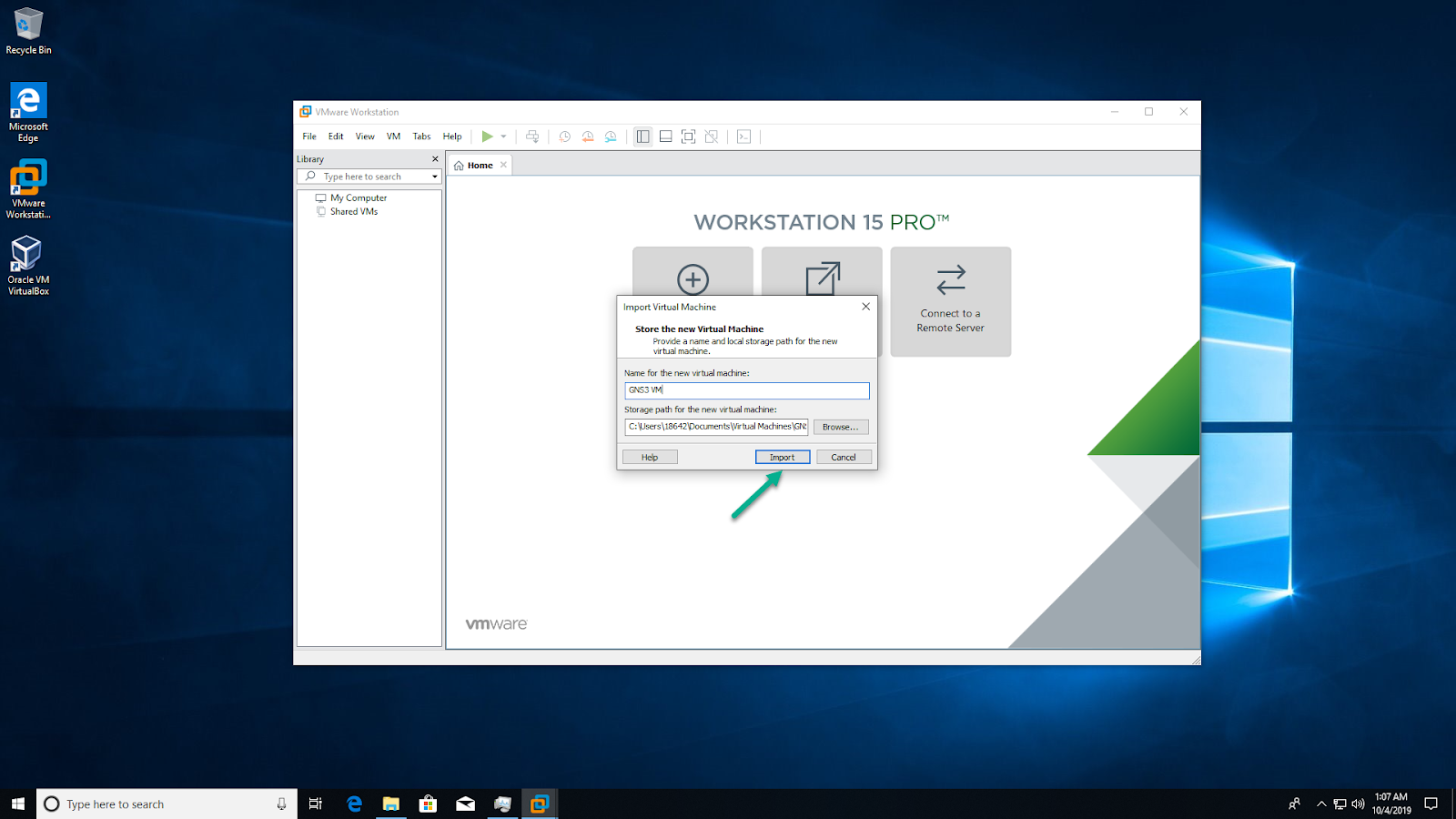
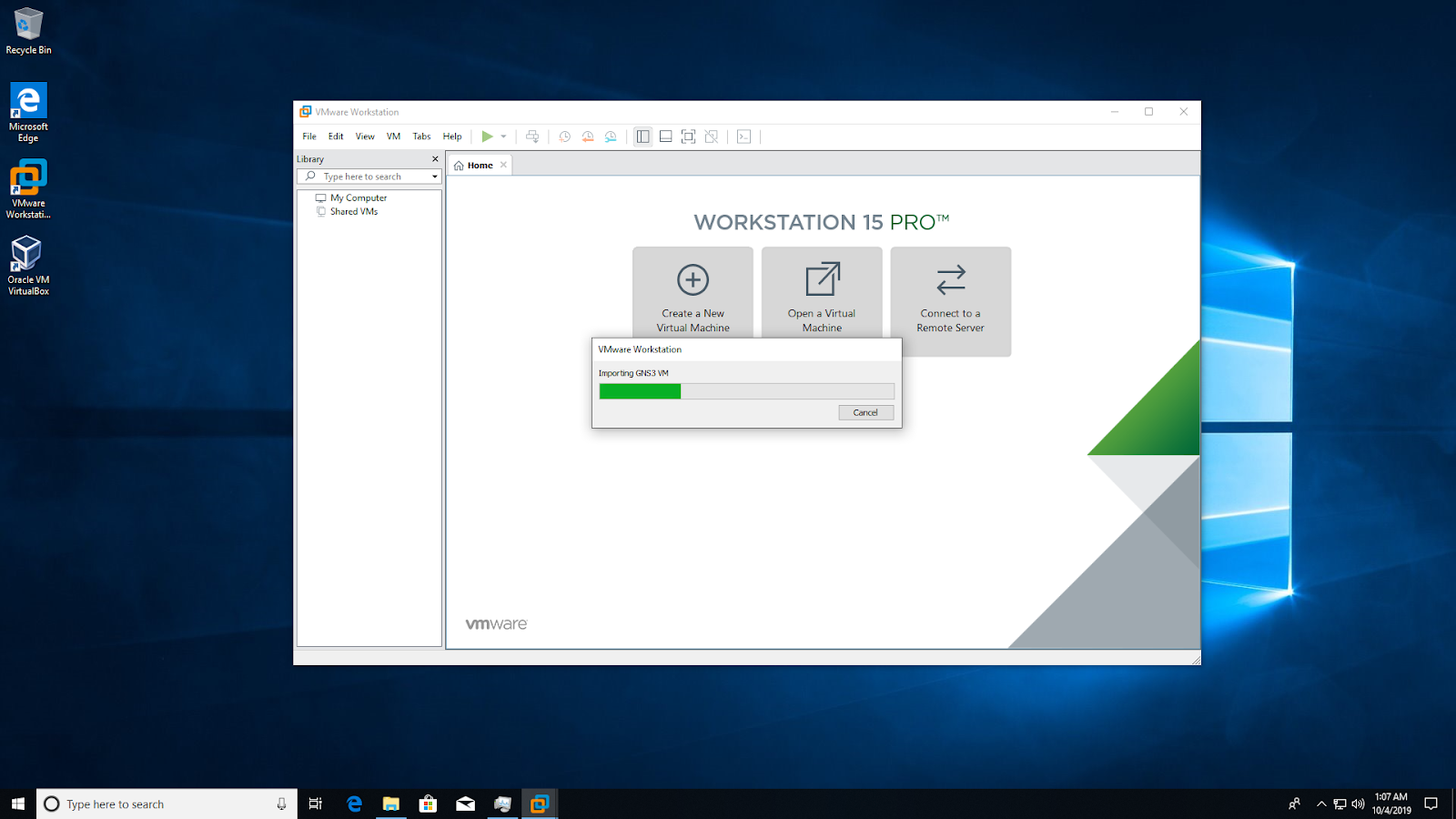
VMware Workstation will import the GNS3 VM:
The GNS3 VM will show as available in VMware Workstation. Leave all settings at their defaults:
Flex-Connect In Detail
It enables customers to configure and control access points (AP) in a branch or remote office from the corporate office through a wide area network (WAN) link without deploying a controller in each office.
The FlexConnect access points can switch client data traffic locally and perform client authentication locally when their connection to the controller is lost.
When AP is changed from local to FlexConnect it will not reboot, but when it is changed from FlexConnect to local it reboots and displays the following error message, “Warning: Changing AP Mode will reboot the AP and will rejoin the controller afer a few minutes. Are you sure you want to continue?” but CLI remains the same. Changing the AP’s mode will also cause the AP to reboot.
Central authentication, local switching—In this state, the controller handles client authentication, and the FlexConnect access point switches data packets locally.
After the client authenticates successfully, the controller sends a configuration command with a new payload to instruct the FlexConnect access point to start switching data packets locally.This message is sent per client. This state is applicable only in connected mode.
Connected Mode When FlexConnect AP can reach Controller, it gets help from controller to complete client authentication.
Standalone Mode When FlexConnect AP cannot reach Controller, it goes into standalone state and does client authentication by itself.
Local Switching Data traffic switched onto local VLANs for an SSID Central Switching Data traffic tunneled back to WLC for an SSID
IPV6 (Internet Protocol Version 6)
What is IPv6?
- Internet protocol version 6 (also called as IPng- IP next generation)
What are IPv6 address? And how they are used?
- IPv6 address are 128 bit address that help in forming networks.
- They are also logical address just like IPv4 address.
- IPv6 address are used to route data from one IPv6 network to another IPv6 network.
Why IPv6 addresses came?
- IPv4 addressing scheme has 4.3 billion (4294967296) IP addresses.
- IPv4 addresses are not enough in future with internet evolution.
- Internet architects knew that IPv4 addresses will get finished with the growth of the internet, and this was the motivation for them to come up with a different IP scheme, which is IPv6 addressing scheme.
- IPv6 is introduced as the IPv4 addresses are being saturated.
What is the motivation for us to move to IPv6?
- It has very large address space. (2^128)
- IPv6 encapsulation is simpler than IPv4, providing faster forwarding rates by routers and better routing efficiency. No checksum is included in IPv6 header.
- There is no broadcast concept in IPv6.
- There are techniques apart from DHCP to automatically assign IPv6 addresses to the end devices.
- Automatic configuration of default gateway occurs on the end devices without the use of protocols like DHCP.
- IPv6 is a plug and play protocol.
- IPsec is in built into IPv6. Two devices can dynamically negotiate security parameters and built a secure tunnel between them with no user intervention.
Differences between IPv4 and IPv6
| IPv4 | IPv6 |
| Internet protocol version 4 | Internet protocol version 6 |
| 32 bit valve | 128 bit value |
| There are 4 octets. | IPv6 addresses have 8 fields. |
| Each octet is made up of 8 bits. | Each field is made up of 16 bits. |
| Each octet is separated using a dot. | Each field is separated using a colon. ( : ) |
| 2^32 IP addresses (4.3 billion) | 2^128 IP addresses |
| Dotted decimal notation | Represented in Hexadecimal notation |
| 192.168.2.1 | 2000:58ab:0000:0000:12cd:0011:8901:13fd |
| Uses Unicast, Multicast, and Broadcast. | Uses Unicast, Multicast, any cast. |
| Classified into A B C D E classes | No classification |
How IPv6 address look like.
- IPv6 address has 128 bits in total.
- IPv6 address have 8 fields.
- Each field of an IPv6 address there are 4 hexadecimal characters.
- So the total number of hexadecimal characters in an IPv6 address are 32.
- Each hexadecimal character is of 4 bits.
IPv6 addressing scheme – simplification:
There are some rules using which you can shorten the length of the IPv6 addresses:
- The leading zeros in a field can be eliminated.
- Example:
- 1200:5600:0028:afcd:0004:0589:0009:ca39
- 1200:5600:28:afcd:4:589:9:ca39
- Example:
- If all the hexadecimal characters are zero within a field, then the whole field can be represented by a single zero.
- Example:
- 2000:0001:0000:0000:0000:000c:00ea:0000
- 2000:1:0:0:0:c:ea:0
- Example:
- If two or more consecutive fields are all zero, then they can be represented by a double colon.
- Example:
- 2000:0001:0000:0000:0000:000c:00ea:0000
- 2000:1::c:ea:0
- Example:
- We can only have a single double colon within an IPv6 address. If :: used more than once, it leads to confusion to identify set of zeros.
Reserved addressees in IPv6:
- Global unicast addresses:
- These are IPv6 public addresses.
- These are provided by the service providers.

- Multicast addresses:

- EIGRP (IPv4): 224.0.0.10
- EIGRP (IPv6): FF02::A
- OSPF v2 : 224.0.0.5, 224.0.0.6
- OSPF v3 : FF02::5, FF02::6
- RIP v2 : 224.0.0.9
- RIP v6(ng) : FF02::9
- Unique local address:
- These are private IPv6 addresses.

- Link local addresses:
- These are very similar to IPv4’s APIPA addresses.
- With these addresses the device cannot communicate out of their networks.
- But in IPv6 link local addresses perform a lot more functionality than APIPA addresses in IPv4.

- Unspecified addresses:
- :: 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0 (since it contains all zeros)
- Loopback addresses:
- ::1 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1
Configuring IPv6 on cisco router:
- Configuring IPv6 addresses on the interface of the router:
- Manual configuration of IPv6 address on an interface (static IP)
- Stateless auto configuration ( EUI-64 )
- Statefull configuration (through DHCP server) (Dynamic IP)
- By default cisco routers do not route IPv6 data.
- By default routers route IPv4 data.
- In IPv6 by default routers acts as IPv6 hosts.
- To enable IPv6 routing on cisco router
- R(config)#ipv6 unicast routing
Stateless auto configuration:

- In stateless configuration the first 64 bits (network portion) of the IPv6 network is sent by router within Router advertisement message, the next 64 bits are calculated using EUI-64 method
- Link local addresses is pre-configured on that interface when we enable IPv6 on that interface of router.
- Link local address : FE80::/10
- First 10 bits are network bits, the next 54 bits all are zeros and the last 64 bits are calculated using EUI-64 method.
- Global unicast addresses are made up of two components
- Subnet ID (64 bits)
- Interface ID (EUI-64 bits)
- Subnet ID contains:
- The registry (which is responsible for assigning it, such as IANA)
- The ISP prefix (which ISP is associated with this address)
- The site prefix (which company is associated with the address)
- The subnet prefix (subnet within the site)
EUI-64 (Extended Unique Identifier – 64)
- EUI-64 is obtained by inserting FF FE in between MAC address of the system to fulfil 64 bits.
- EUI-64 (Extended unique identifier 64)
- Step 1
- MAC address (48 bit value)
- FFFE (16 bit value)
- Step 2
- Insert the FFFE value between the MAC address.
- 48 bit MAC address
- 24 bits FFFE 24 bits
- Insert the FFFE value between the MAC address.
- Step 3
- 7th bit from the start is inverted.
- Step 1
- EUI-64 (Extended unique identifier 64)
Note: In the MAC address the following bits have some identification.
7th bit: (G/L) (Global/Local) 8th bit: (I/G) (Individual/Group)

IPv6 addressing scheme:

WAN Technologies
What Is WAN?
- Wide area network.
- Communication between LANs which are in distant areas like different cities, different countries. (geographically far from each other)
- Service provider network is the transit area in WAN.
- Customer need to pay money to the service provider.
- Amount depends on speed and distance of the WAN link.
- LANs and WANs are different at the data link layer and physical layer.
- Standards:
- American standard
- E1 : 2 Mbps.
- European standard
- T1 : 1.5 Mbps
- T3 : 45 Mbps
- American standard
WAN connection types:
- Leased lines
- A pre-established, private connection from one site to another through a service provider’s network.
- Also called as a dedicated circuit or dedicated connection.
- Always a point to point connection between two end points.
- Used when there is a constant flow of data, or when a dedicated amount of bandwidth is required.
- Leased line is secured reliable, always up, dedicated connection.
- Billing is done on 24/7 basis.
- PPP and HDLC are used as WAN protocols.
HDLC and PPP: (HDLC & PPP are WAN link encapsulation protocols)
- HDLC:
- High level data link control
- Cisco proprietary protocol
- Provides error detection
- Doesn’t support authentication
- No data compression
- HDLC is the default encapsulation on serial interfaces
- PPP
- Point to point protocol
- Open standard
- Supports authentication
- Data compression
- PPP has three main components
- Frame format (encapsulation)
- Link control protocol
- Network control protocol
- Multilink
- LCP and NCP are responsible for establishing, configuring, authenticating and testing PPP connection.
- LCP:
- To send and receive keep alive messages through the leased line to know if the other end is available.
- LCP also helps PPP to find that which features both sides are using, and if they don’t use the same features then the link will not come up.
- NCP:
- The routers negotiate with each other that which layer 3 protocols data they will be sharing through the PPP link.
- PPP authentication:
- PPP uses two methods to support authentication: PAP and CHAP.
- PAP – password authentication protocol
- Simplest but less secure
- Two way hand shake process
- Source send its username and password in clear text to destination.
- Destination compares username and password with its data base.
- If it matches then sends accepts message otherwise sends reject message.
- CHAP – challenge handshake authentication protocol
- Three way hand shake process & secure than PPP.
- Source sends its username to destination.
- Destination looks at username/password in its database and generates a challenge value using MD5 and sends that value to source.
- Source uses that challenge and generates a hash value and send it to the destination.
- Destination verify this hash value and sends accept or reject message
- Password is never sent on that link to provide security.
- PAP – password authentication protocol
- Circuit switching:
- A dialup connection through a provider’s voice-grade connection.
- Either uses an analog modem or an ISDN connection
- Used when a slow speed connection is needed, or there is no need to transfer a lot of data.
- One call establishes a circuit to one destination site
- Establishes logical circuits between source and destination (circuit switching)
- PPP, HDLC and SLIP are the protocols used in circuit switching
- Example:
- PSTN – Public switched telephone network
- ISDN – Integrated service digital network
- Packet switching: (Frame Relay)
- Contains all features of leased line and ISDN
- Virtual circuits (VCs) reduced no of leased lines significantly
- PVC and SVC offers flexibility
- Very economical
- Billing can be done on any basis
- Suitable for all scenarios (high bandwidth)
- Availability is an issue
- No frame relay technology in India.
Frame Relay Terminology:
- FRS – Frame relay switch
- The switch used at service provider end in frame relay network.
- VC – Virtual circuit (a logical circuit establish between FRS)
- Logical connection between two FRS
- PVC – Permanent virtual circuit
- The VC that is always available. Similar to dedicated line.
- SVC – switched virtual circuit
- The VC that established when needed. Similar to ISDN
- DLCI – Data link connection identifier (tag attached to VC for identification)
- It is identification for VC. Range is 16 – 1007
- The DLCI no’s are assigned by the service provider’s.
- CIR – committed information rate
- The bandwidth committed by Service provider
- The max allowable bandwidth through the PVC from one to another
- Each PVC can have a unique CIR.
- LMI – local management interface (keep alive messages)
- Signals checks the keep alive status: DTE to DCE
- Signalling between routers and frame relay switches
- LMI does not travel across the entire PVC from one end to another
- LMI types: q933a, cisco, ANSI…
- FECI – Forward explicit congestion notification
- Messages to FRS and source if congestion occurs between FRS and destination
- BECI – Backward explicit congestion notification
- Messages to FRS and destination if congestion occurs between FRS and source
- BE – burst excessive (boosting bandwidth)
- Frame relay boosts the bandwidth of VC if network is free.